Biomedical engineering is at the forefront of revolutionizing healthcare, combining principles of engineering, biology, and medicine to develop innovative solutions that improve patient outcomes. As technology advances, the field is evolving rapidly, introducing groundbreaking trends that promise to transform diagnostics, treatment, and patient care. From artificial intelligence (AI) to personalized medicine, the future of biomedical engineering is poised to address some of the most pressing challenges in healthcare. This article explores emerging trends in biomedical engineering and their potential to enhance patient outcomes.
The Role of Biomedical Engineering in Healthcare
Biomedical engineering bridges the gap between technology and medicine, creating tools, devices, and systems that improve healthcare delivery. From imaging equipment and prosthetics to wearable devices and telemedicine platforms, biomedical engineers play a critical role in advancing medical science. As healthcare demands grow, the field is shifting toward more personalized, efficient, and accessible solutions.
Emerging Trends in Biomedical Engineering
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming healthcare by enabling faster and more accurate diagnostics, predictive analytics, and personalized treatment plans. In biomedical engineering, AI is being used to analyze medical images, predict disease progression, and optimize treatment protocols. For example, AI-powered algorithms can detect early signs of diseases like cancer or heart conditions from imaging data, improving early intervention and patient outcomes.
2. Wearable and Implantable Devices
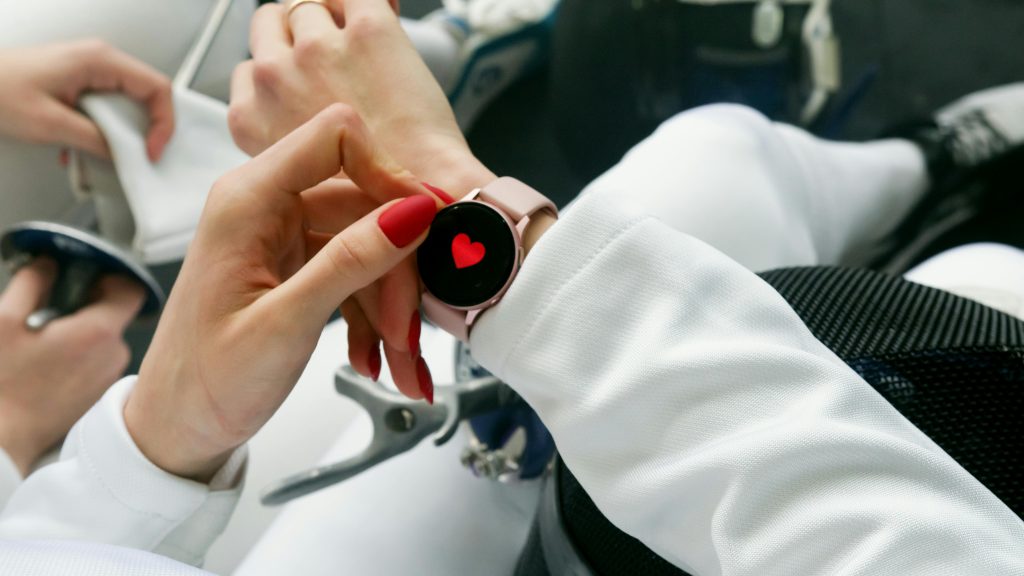
Wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering real-time monitoring of vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels. Implantable devices, such as pacemakers and neural implants, are also advancing, providing targeted treatment for chronic conditions. These technologies empower patients to take control of their health and enable healthcare providers to monitor patients remotely.

3. 3D Printing in Medicine
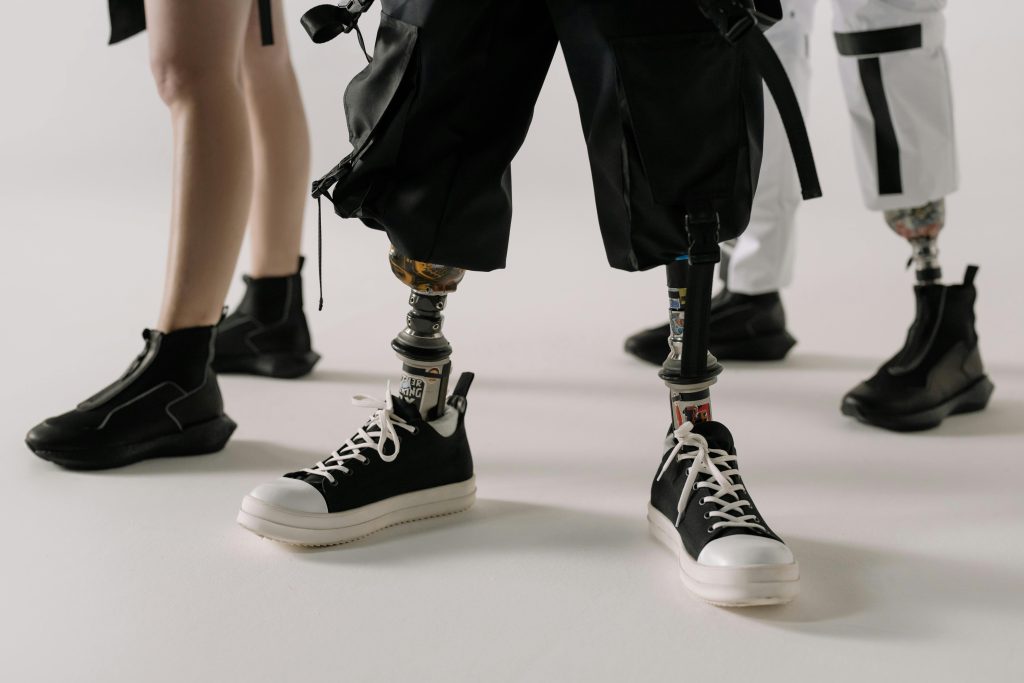
3D printing is revolutionizing biomedical engineering by enabling the creation of customized prosthetics, implants, and even tissues. This technology allows for patient-specific solutions, improving the fit and functionality of medical devices. For example, 3D-printed prosthetics are tailored to an individual’s anatomy, enhancing comfort and mobility.

4. Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
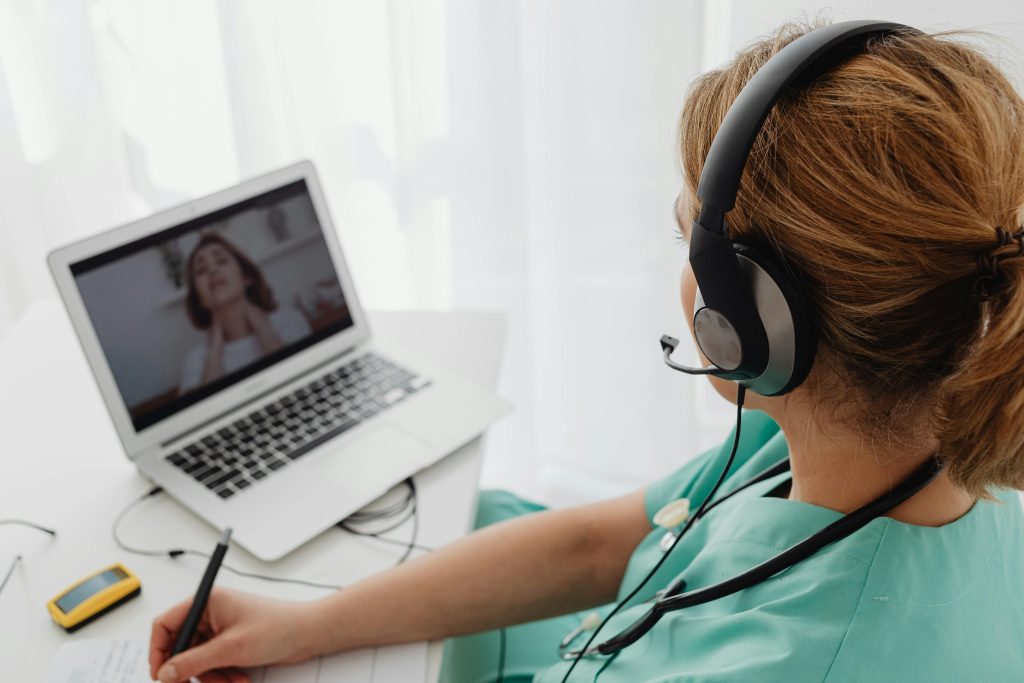
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine, and it is now a permanent fixture in healthcare. Biomedical engineers are developing advanced telemedicine platforms and remote monitoring systems that allow patients to consult with healthcare providers from the comfort of their homes. These technologies are particularly beneficial for patients in rural or underserved areas.

5. Personalized Medicine
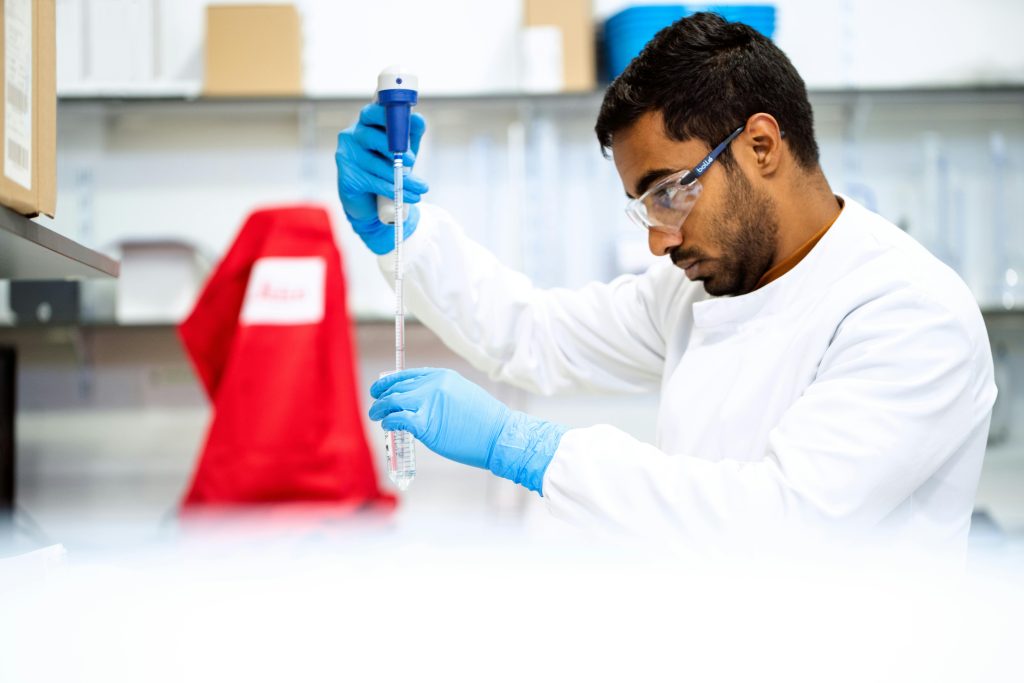
Personalized medicine tailors treatments to an individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health conditions. Biomedical engineers are developing tools like genomic sequencing devices and AI-driven diagnostic systems to support this approach. Personalized medicine ensures that patients receive the most effective treatments with minimal side effects.
6. Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering
Regenerative medicine focuses on repairing or replacing damaged tissues and organs. Biomedical engineers are working on innovations like bioengineered tissues, stem cell therapies, and organ-on-a-chip models. These advancements hold the potential to treat conditions like spinal cord injuries, heart disease, and organ failure.

How These Trends Improve Patient Outcomes
- Early Diagnosis and Intervention: AI and advanced imaging technologies enable early detection of diseases, improving treatment success rates.
- Personalized Care: Wearable devices and personalized medicine ensure that treatments are tailored to individual needs, enhancing effectiveness.
- Accessibility: Telemedicine and remote monitoring make healthcare more accessible, especially for underserved populations.
- Improved Quality of Life: Innovations like 3D-printed prosthetics and regenerative medicine restore functionality and improve patients’ quality of life.
The Future of Biomedical Engineering
The future of biomedical engineering is bright, with several trends shaping the field:
Integration of AI and Big Data
AI and big data will continue to drive innovation, enabling predictive analytics, precision medicine, and automated diagnostics.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology holds promise for targeted drug delivery, early disease detection, and minimally invasive treatments.
Collaboration Across Disciplines
Biomedical engineers will increasingly collaborate with data scientists, biologists, and clinicians to develop holistic solutions.
Focus on Sustainability
Sustainable practices, such as eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient devices, will become a priority in biomedical engineering.
Conclusion
Biomedical engineering is transforming healthcare by introducing innovative technologies that improve patient outcomes. From AI-driven diagnostics to personalized medicine and regenerative therapies, these advancements are addressing some of the most significant challenges in healthcare. As the field continues to evolve, it will play a pivotal role in creating a healthier, more equitable future for all. The future of biomedical engineering is not just about technology, it’s about improving lives and ensuring better patient outcomes.
References
- “The Role of AI in Healthcare” – Nature Medicine
- “Advancements in Wearable Health Technology” – IEEE Spectrum
- “3D Printing in Medicine: Current Applications and Future Trends” – ScienceDirect
- “Personalized Medicine: Transforming Healthcare” – National Institutes of Health (NIH)